Osteochondrosis in the spine is a disease caused by the destruction of bone and cartilage tissue in the cervical, chest and lumbar spine.
First, as the disease progresses, the central part of the spinal disc is modified - SO is called the jet core. Therefore, the vertebrae develops some astonishing properties along the annex around the disk, and creates fines and cracks on the annex.
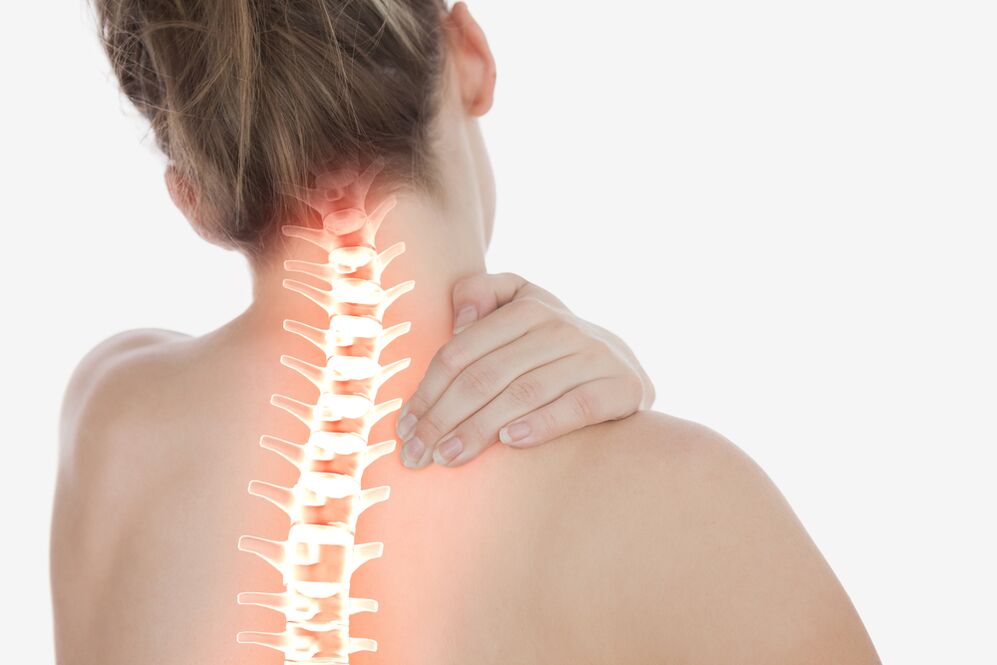
Further progress in osteochondrosis in the spine can lead to complications of the disease - herniation of the intervertebral disc or rupture of annulus fibrous fibrous hernia and vertebral hernia. The instability of the spine in affected areas leads to head pain and limited migration in the osteocartilage degeneration of the cervical vertebrae, as well as limited body mobility in the body, osteochondria in the chest spine and lumbar spine.
In 75% of cases, osteochondrosis in the spine is the cause of back pain. The risk of spinal malnutrition increases significantly as you age, so on average, symptoms of spinal osteocartilage degeneration are observed in every inhabitant of the Earth over 30 years old.
Causes of spinal osteocartilage degeneration
Under vibrating conditions, through hard physical work or professional employment, the provocative factor of spinal osteochondrosis development is considered as back injury or systemic load on the back. If you have to do a lot of loading and unloading work, buy hydraulic collection for your car.
Early manifestations of spinal osteochondria symptoms are caused by weak body development, flat feet, or excessive weight. There is also a genetic tendency to be genetically oriented to the loose structure of the intervertebral disc and abnormal spinal structure. Intensive training in gyms violates the rules of back load distribution, and a sedentary lifestyle and improper nutrition are not good for spinal health.
Symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis
The disease manifests as many typical symptoms. Spinal osteochondrosis is characterized by back pain, numbness of the affected spine, a decrease in motion amplitude, increased severity, rapid movement, increased pain when coughing or snot or sneezing.
Chronic pain is one of the symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis and can lead to increased fatigue. When the spine is used to compress the nerve roots of the spine, the pain may be more intense and sharp. In this case, its localization is not limited to the dorsal area, but is felt by one person in the limb area.
Osteochondrosis stage of the spine
The stage of the disease depends on the severity of the symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis. In the first stage of osteochondral toxin in the spine, there is no real pain if the spine is light and has weak stability. The destruction of the annulus, the reduction in the size of the vertebrae cracks, and pain of various intensities are symptoms of the second stage of spinal osteochondrosis.
The third stage of the disease is characterized by significant deformation of the bone and vertebral tissue until the advent of vertebral hernia. The most severe stage 4 spinal osteochondria symptoms are mass bone growth, limited mobility, severe pain, and complete or partial paralysis of the limbs caused by nerve root compression.
Symptoms of cervical vertebrae
Osteochondrosis in the cervical vertebra usually leads to blood circulation diseases due to compression of the arteries. This leads to nervous headaches, dizziness and fainting. Osteocartilage degeneration in the vertebrae spine is sometimes observed, and sometimes vertebral artery syndrome is sometimes observed. It is characterized by head noise, the image of "flies" or the colorful spots in front of the eyes. Because of the osteocartilage of the cervical spine, pain around the shoulder or hand is also possible.
Symptoms of thoracic vertebrae
The osteocartilage of the chest and spine can aggravate various cardiac pathological processes. This disease can lead to the progression of intermittent neuralgia (squeezing the intermittent nerve). The bone cartilage of the spine in the chest becomes, chest pain and the feeling of "wooden stake" in the center of the chest.
Symptoms of lumbar vertebrae

Osteocartilage in the lumbar spine can lead to the development of the following diseases: cashew nuts and hernia.
Ishias is one of the complications of lumbar osteochondrosis, characterized by sciatic nerve injury, pain in the buttocks area, hypotension (reduced tension) in the calf and gluteus muscles.
Cashew nut symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis, severe pain in the lower back due to displacement of the vertebrae or loss of the spinal disc.
Lumbar epinephrine is another complication of lumbar osteocartilage degeneration, which is caused by a hernia in the lowest intervertebral disc of the spine. It is accompanied by pain in the hips, radiation in the back of the thighs, holes under the knees, holes under the lower legs and holes under the feet.
Diagnosing osteochondral disease in the spine
Neurologists established a preliminary diagnosis of "spine osteochondrosis" when first examining complaints related to the patient's back pain and limited mobility. The stage of spinal osteocartilage degeneration is determined based on the degree of spinal deformation, the patient's posture, and the number of affected discs.
All the above-mentioned symptoms of osteochondrosis are diagnosed by sensing the patient's back. Doctors also pay attention to the state of muscle tone. Because in most cases, this disease is accompanied by hypertonicity of the back muscles.
Using tests to bend the spine, the amplitude of the patient's movement was determined. Thanks to the use of X-ray, CT and MRI, the diagnosis was specified and future strategies for spinal osteochondria disease were identified.
Treatment of osteochondral disease in the spine
Conservative and surgical methods are used in the treatment of osteocartilage of the spine. The purpose of both is to eliminate pain syndrome and prevent further development of spinal deformation.
At the same time, surgical treatment of spinal osteochondrosis is only used when conservative treatments for the disease are ineffective.
The active phase of the application of conservative methods lasts on average for 2 months. At the beginning, short-term increase in pain syndrome is due to the body’s response to medications, physical therapy exercise (movement therapy), and physical therapy. Massage, manual treatment, extract and reflexology are also used in conservative treatment of spinal osteochondrosis. The effectiveness of the treatment of spinal osteochondrosis depends on the patient's own systemic nature and perseverance in performing the exercise therapy complex.
The surgical treatment of spinal osteochondrosis is performed with hernia of the intervertebral disc, which lasts for up to 6 months. The instructions of this operation also reduce the gap between the vertebrae to 1/3 of the initial size and compression of the spinal cord root.
The main method of surgical treatment of spinal osteocartilage is discectomy, which means removing deformed intervertebral discs. This operation can be minimized using the differential resection method B-TWIN system and laser evaporation of the nucleus of the deformation disk.
After surgical treatment of osteochondrosis in the spine, the recovery period is expected to last for 6 months. During this period, the patient was directed to a nursing home for physical therapy, manual therapy, acupuncture, etc.